History of Native America
Maeve Kane
mkane2@albany.edu
maevekane.net/hill
revisionist history
- history is an evolving field of study
- history is an argument about how we know what we know
- history is inherently political - what is emphasized and how
- settler colonialism is the process of writing Indigenous perspectives out of their own histories
The Civilizing Mission
First half
- Indian education
- Playing Indian
- Anthropology and Indian history
where are we?
- Entanglement era: 1650-1770
- Removal era: 1770-1840
- Extermination era: 1840-1887
- Allotment & Assimilation era: 1887-1940
- Termination era: 1940-1975
- Self-Determination era: 1975-present
Ursuline Convent, Quebec 1620-1830
Eleazar Wheelock and alumni, 1750-1780

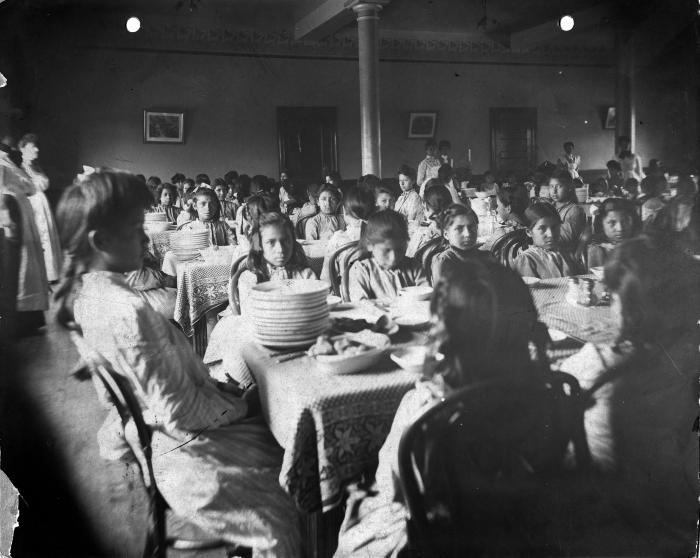
Thomas Indian Orphan Asylum, 1840-1970
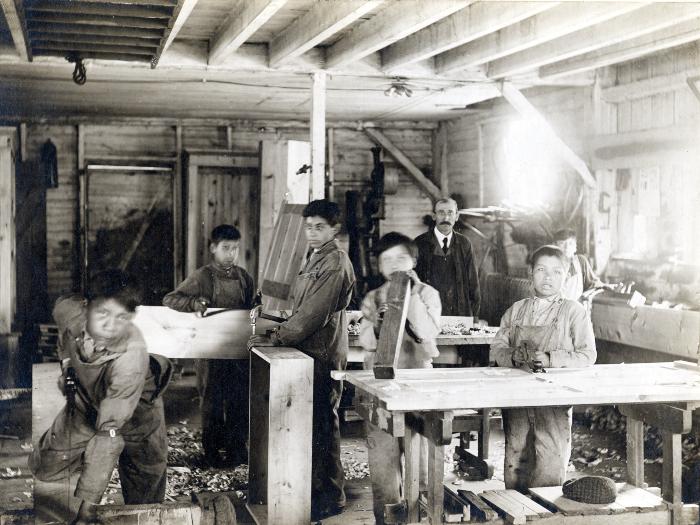

Thomas Indian Orphan Asylum, 1840-1970
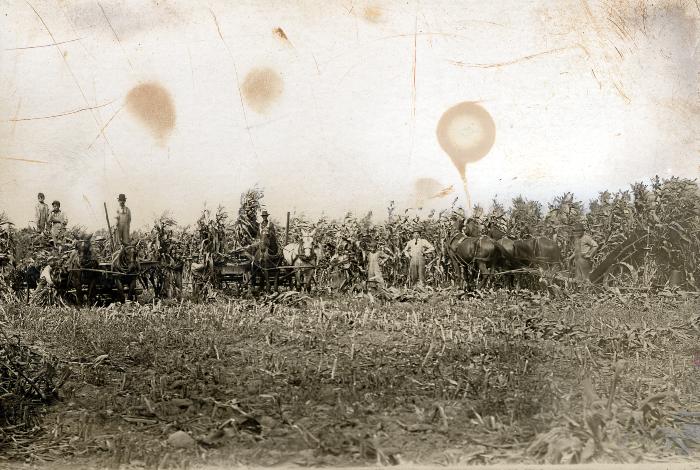

Thomas Indian Orphan Asylum, 1840-1970
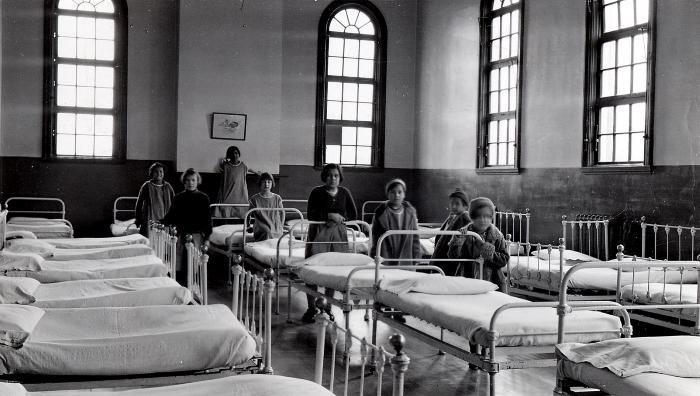
Thomas Indian Orphan Asylum, 1840-1970

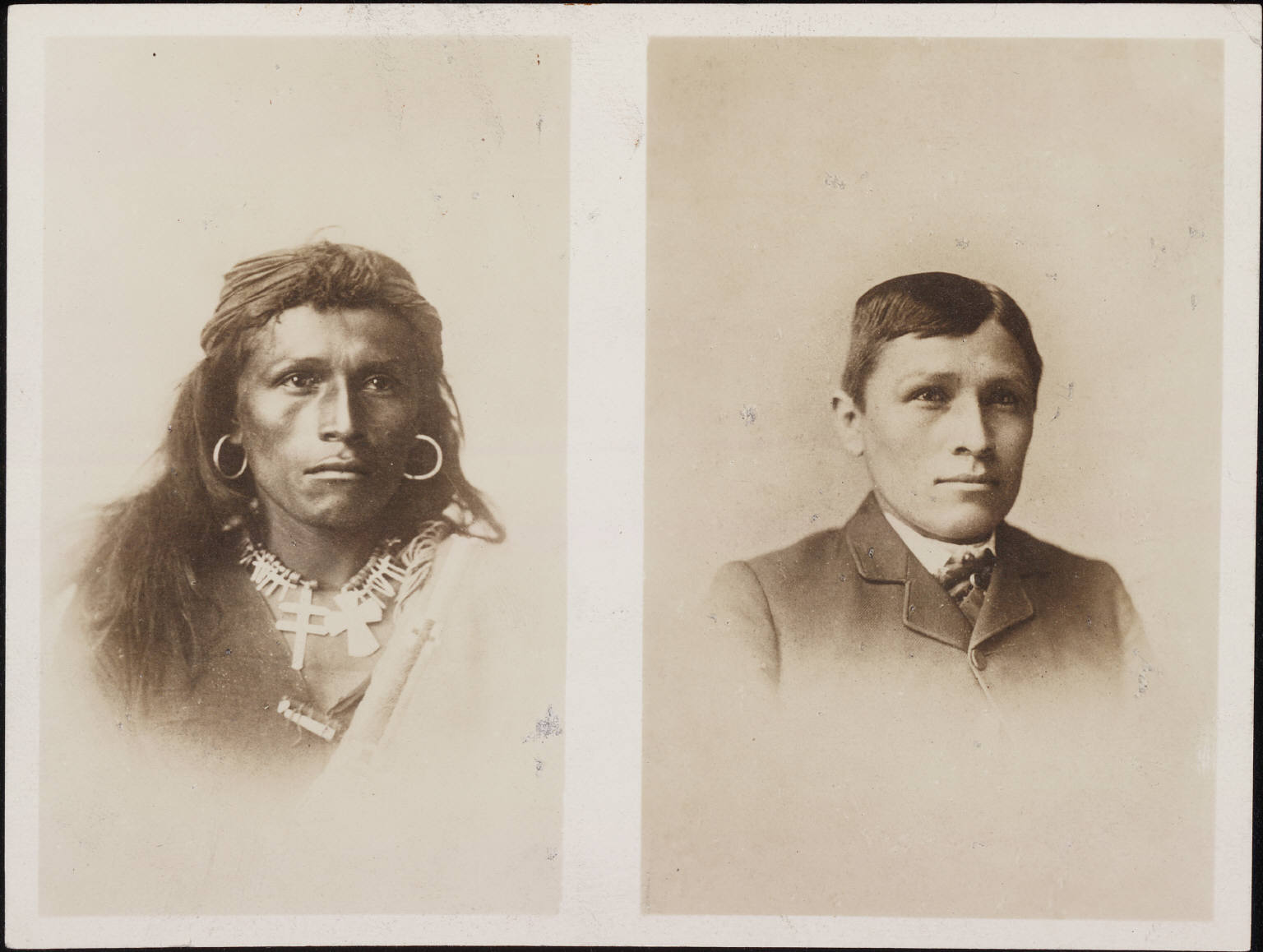
Tom Torlino

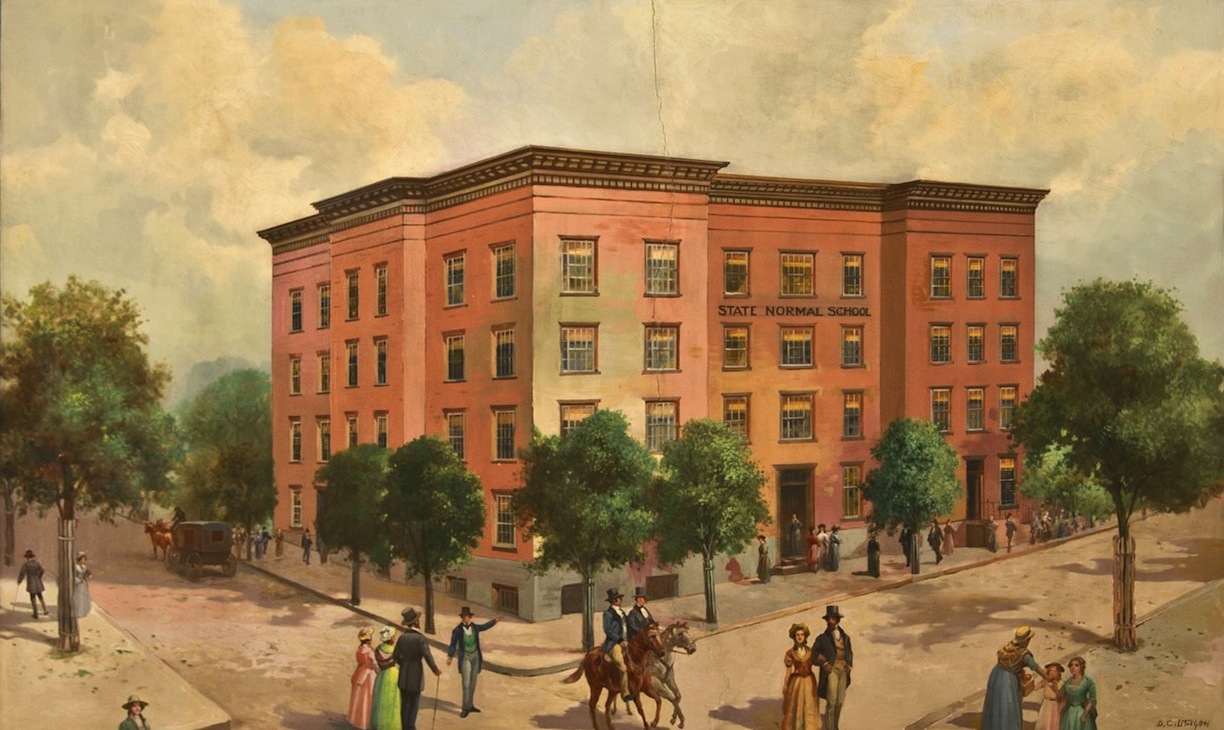
Albany State Normal School, 1844-present

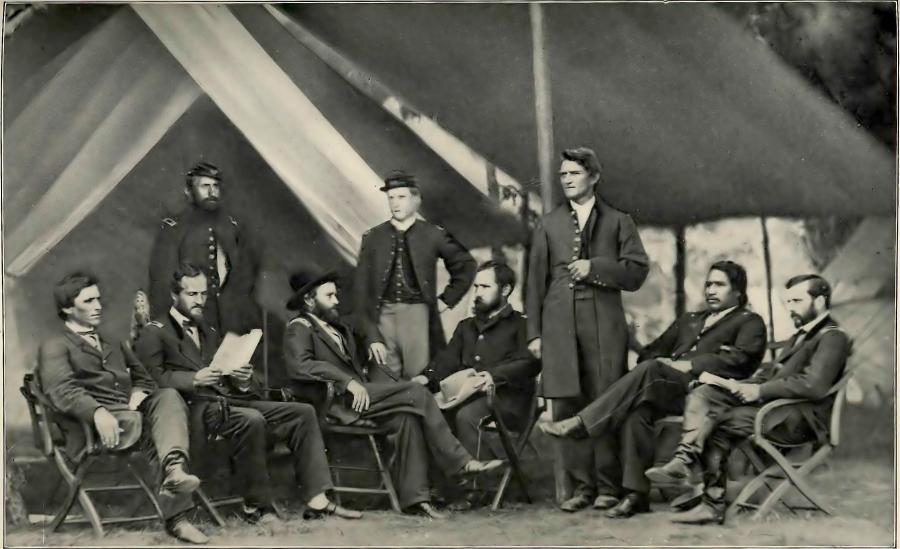
Ely Parker

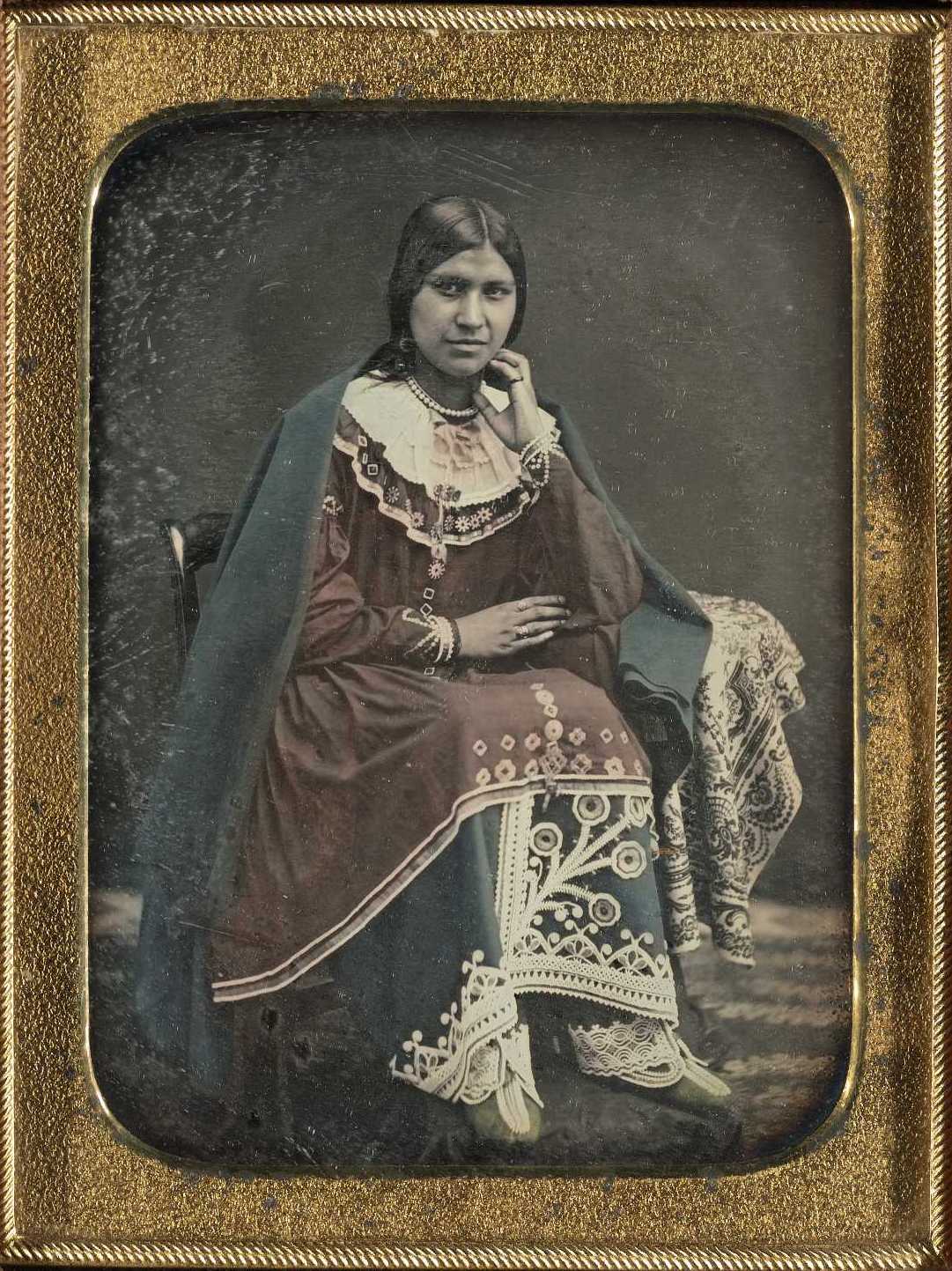
Caroline Parker

Lewis Henry Morgan
- upstate NY, 1830s-1860s
- Ely Parker's bro
- "Tammany Indians": secret fraternal organizations
- Indians are disappearing and their virtues must be saved
- virtuous whites can embody the best characteristics of the "original Americans"
Scouting and Playing Indian
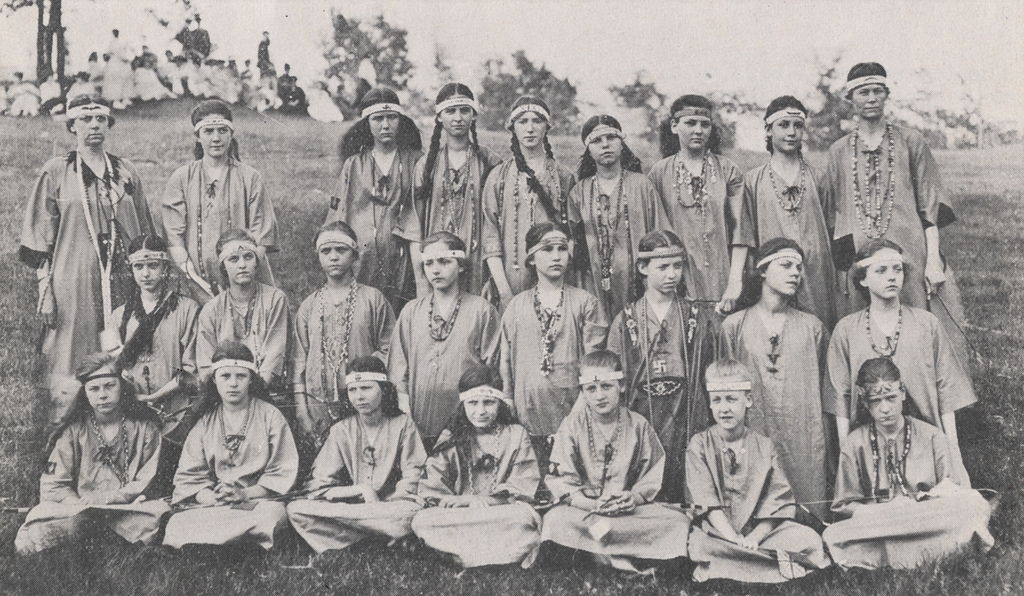

Scouting and Playing Indian
- cities are dangerous to health
- nature & health of white workers
- anti-child labor activism
- need for boys trained with skills for colonial wars
- military uniforms for discipline (Carlisle)
- constructs universal “Americanness” for immigrant whites, Hispanic and African Americans
HOW DOES THIS MAKE SENSE?
- Americans play Indian to become "truly American"
- playing Indian gives symbolic claim to land, stewardship, positive stereotypes
- allows Americans to make a distinction between "good Indians" and "bad Indians"
- good Indians disappear; bad Indians are violently removed
- land is therefore free for settlement
- justifies and erases colonial violence
legacies
- language and cultural loss
- family disruption
- religious & institutional sexual abuse
- paths out of poverty for some
- Pan-Indian political organizing: Society of American Indians & National Congress of American Indians
- legal, medical and academic skills to benefit reservations
INDIAN CHILD WELFARE ACT: 1978
- 25-35% of children removed between 1886-1976
- UN Declaration of Rights of Indigenous People
- states have jurisdiction over child welfare
- guarantees tribal jurisdiction over cases on reservations or with enrolled member parents
- 2013 SCOTUS Adoptive Couple v Baby Girl
Second half
- Cherokee Removal: big picture
- Cherokee Removal: legal
- Cherokee Removal: legacies
- Iroquois non-removal
Cherokee background
- Proclamation of 1763: British Indian policy
- Treaty of Paris 1783: end of American Revolution
- Commerce clause of Constitution
- doctrine of conquest: basis of all US land ownership
- Missouri Compromise 1820: westward spread of slavery
Constitutional COMMERCE CLAUSE
To regulate Commerce with foreign Nations, and among the several States, and with the Indian Tribes
1823: Johnson v M'Intosh
- discovery doctrine & doctrine of conquest
- Native American right of occupancy
1830: Cherokee Nation v Georgia
- Cherokee Nation does not have standing
- not a foreign nation, domestic dependent nations
1832: Worcester v Georgia
- states may not make treaties or enforce laws
- only federal government may make treaties
THE TREATY PARTY
- John Ridge, Elias Boudinot & Stand Watie
- "full blood," traditional govt
- protect sovereignty by getting away from Georgia
THE NATIONAL PARTY
- John Ross, Major Ross, William Hicks
- intermarried, slave-owning, elected govt
- protect sovereignty by working within US system
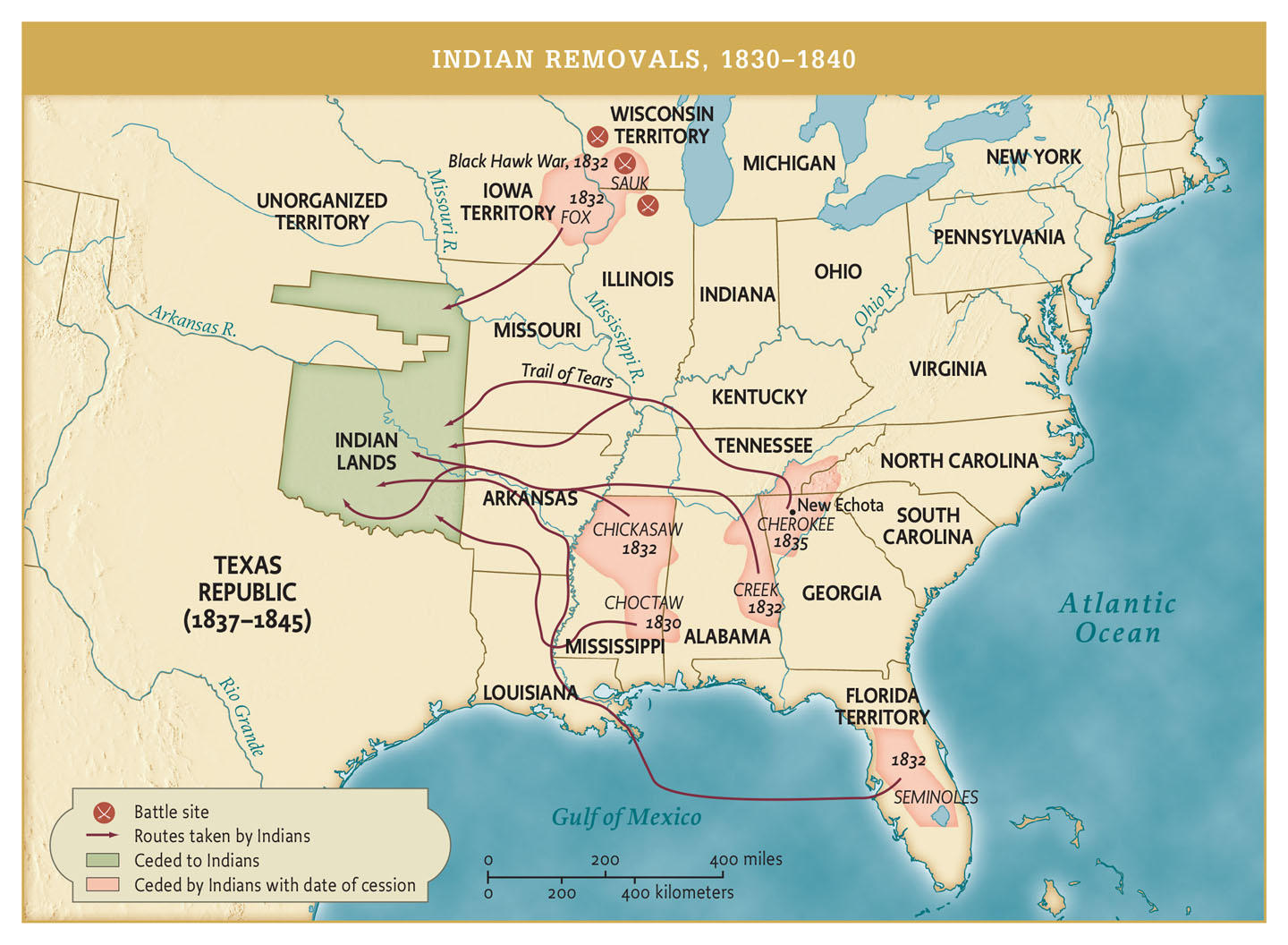
TREATY OF NEW ECHOTA 1835
- Oct 1835: John Ross + Elias Boudinot attempt to negotiate in DC
- Dec 1835: treaty council convened in Georgia
- signed by 21 with no legal authority
- citizenship clause removed after signing
- Ross petitions Congress: 16k signatures
TRAIL OF TEARS
- hot dry fall, cold wet winter
- 7k militia to remove 13k Cherokees
- 3 months, 1000mi, 1/4 mortality rate
- Ridge, Boudinot & Watie murdered in Oklahoma
- was there an alternative?
CIVIL WAR LEGACY
- 1860 Indian Territory opened to white settlement
- Confederacy promises to recognize Indian nations as independent nations
- security of land and property: slaves
CHEROKEE FREEDMEN
- Treaty of 1866: former slaves to be made citizens and given land
- Dawes Rolls problems
- Indian Self Determination Act vs. 13th Amendment?
- 2017 reinstatement
- is Cherokee citizenship biological or political?
SEMINOLE (NON) REMOVAL
- First Seminole War: harboring slaves
- Second: enforcement of Indian Act
- Third: white squatting on reserved lands
- Confederate recognition
- Florida Everglades Natl Park
IROQUOIS (NON) REMOVAL
- who has right of discovery to 1776?
- who has the power to negotiate 1776-1783?
- Mass. sold purchase rights to private companies
- Iroquois rented land to whites who refused to move